Methods of improving saline soil
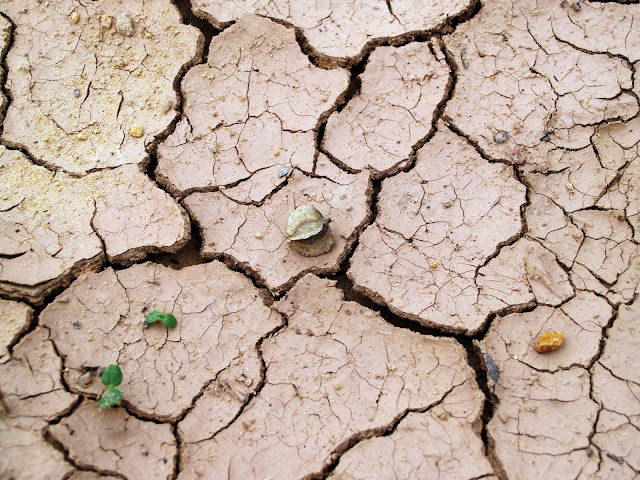
Saline-alkali soil is a collective term for all kinds of saline soil, alkaline soil, and different degrees of salinization and alkalization. Because the soil contains a lot of saline and alkali components, and has poor physical and chemical properties, the growth of plants is inhibited or even unable to grow. Improving and using saline-alkali land is of great significance to compensate for the decreasing area of arable land and ensure food security.
The harm of saline soil
1. Salinization deteriorates the physical and chemical properties of the soil, and the living conditions of crops, forest trees and pastures deteriorate, which are manifested in:
① The content of soil organic matter is relatively reduced. Because soil salinization inhibits the process of soil herbification and the accumulation of soil organic matter, the content of soil organic matter is relatively reduced, which affects the physical and chemical properties of the soil.
②The soil nutrient condition becomes worse. Under the influence of drainage, salt washing and increased quota irrigation, soil nitrogen loss is serious. Organic matter is the main source of soil phosphorus. The decomposition products of organic matter can release phosphorus and improve its effectiveness. Saline-alkaline soil has low organic matter content. The content of available phosphorus is also low. In addition to the high pH value of saline soil and high calcium carbonate content, phosphorus in the soil easily forms insoluble phosphates, thereby reducing the effectiveness of phosphorus. In addition, trace elements such as zinc, manganese, iron, and copper It also reduces the effectiveness due to the high soil pH.
③ Poor soil physical properties. Saline-alkali soil has poor structure, larger diameter, less non-capillary pores, poor cohesiveness, poor moisture retention, high soil colloidal Na+ content, poor water permeability, difficult soil gelation, low soil effective water content, and significant increase in ineffective water content. Water supply Poor ability, low ground temperature in spring and autumn, and cold soil, affecting timely crop planting and seedling growth, and high ground temperature in summer, which accelerates surface evaporation and salt accumulation.
④The soil microbial activity is inhibited by salt and alkali. There are few N-fixing bacteria and nitrifying bacteria, and the activity is poor, so the ammonification and nitrification in the soil are weak.
2. Soil solution directly poisons crop cells
Due to the high concentration of saline-alkali soil solution and high osmotic pressure, the ability of crops to absorb water and nutrients is reduced. At the same time, the ability of plant roots to selectively absorb nutrient ions is correspondingly reduced. Therefore, a large number of non-nutrient ions enter the body while nutrient ions are absorbed. Reduce or not absorb, thereby disrupting the normal ion balance in the body, interfering with the normal metabolic function of crops, destroying the synthesis and hydrolysis of protein, causing the accumulation of ammonia and soluble salt ions in the body, resulting in ion poisoning and endangering crops Growth and development, and even death. The degree of harm of different salts is different. The order of the harm of several common soluble salts to crops is: sodium carbonate>magnesium chloride>sodium bicarbonate>sodium chloride>sodium sulfate.
3. Poor crop growth causes seedling shortage, yield reduction, and death
According to general statistics, crops in non-salinized soil do not lack seedlings and yields are normal, lightly saline soil lacks seedlings by 10-20% (average 15%), and medium-saline soil lacks seedlings by 20-50% (average 35%). In the heavy saline soil, the lack of seedlings will reduce the yield by 50-80% (65% on average), and the saline soil can only survive individually without harvest. Based on the salinization area of the irrigated area and the current annual crop planting ratio, a rough estimate of the annual crop loss in each irrigation area: 44 million kg of cotton, about 500 million yuan, and 700 million yuan of planting losses due to salinity, accounting for about the total agricultural 26% of output value.
Principles of fertilization in saline soil
The principle of fertilization for saline soil is to control the use of low-concentration fertilizers. Organic fertilizer contains a lot of organic matter, which buffers harmful anions and cations in the soil, and is good for rooting and promoting seedlings. High-concentration compound fertilizer has few ineffective components and few residues, but the amount of chemical fertilizer should not be too much each time to avoid aggravating the secondary salinization of the soil. After applying the chemical fertilizer, it should be combined with irrigation to reduce the concentration of the soil solution.
Methods of improving saline soil
1. Wash salt
Salt washing is to pour water into the saline-alkali soil to dissolve the soil salt, and drain the soluble saline-alkali in the topsoil layer into the deep soil through infiltration or leaching out, and then infiltrate it into the drainage ditch for removal.
2. Level the land
Leveling the land can make the water infiltrate evenly, improve the effect of raining and irrigation to wash the salt, and prevent the soil from spotting salinization.
3. Deep ploughing and deep turning
The distribution of salt in the soil is that the surface layer is more and the lower layer is less. After plowing, the salt in the top soil can be turned to the bottom of the plough layer, and the soil with less salt in the lower layer can be turned to the surface. Plowing can loosen the cultivated layer, cut off the soil capillary, reduce soil moisture evaporation, and effectively control soil return to salt. The best time to plow saline soil is spring and autumn. Spring and autumn are the seasons when the salt returns to heavier. Plowing in autumn is especially helpful for killing pests and eggs, removing weeds, burying roots and stubble deeply, strengthening the decomposition of organic matter and the release of late-acting nutrients, so it is worth promoting.
4. Rake the ground in time
Harrowing the ground can loosen the topsoil, cut off the soil capillary water to transport salt to the surface, and play a role in preventing salt return. The harrowing of the land should be timely, shallow spring ploughing, rush ploughing, early autumn ploughing, dry ploughing instead of wet ploughing.
5. Farmland water conservancy improvement measures
Farmland water conservancy improvement measures use fresh water leaching measures to wash the soil salt, and then drain the salt out of the soil through drainage measures, reduce the groundwater level, reduce the accumulation of salt on the soil surface, and achieve the purpose of improving saline-alkali land. This is the current saline-alkali land improvement The most effective measure in the Water conservancy engineering measures such as combining wells, ditches and canals, or burying concealed pipes in areas with higher groundwater levels, using more rainfall, surface water irrigation, or pumped groundwater irrigation by motorized wells, can leaching the salt in the surface soil to the tillage. At the same time, there will be a large drop in the groundwater table below the surface layer, and the groundwater table shall be controlled below the critical water level during the strong salt return season to reduce the salt return of the surface soil. my country has done a lot of work in improving saline-alkali soil in water conservancy projects, and has achieved remarkable results, especially in the comprehensive utilization of drainage, irrigation, storage, and supplementation in the Huanghuaihai Plain area of my country, and the hidden pipe salt drainage in the coastal area. The unified regulation of rainwater, surface water, soil water and groundwater has greatly accelerated the comprehensive treatment process of drought, flood, saline-alkali and saline water.
Choose an effective soil conditioner
1.Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is a metabolite of phenylalanine and a new type of natural phenolic plant regulator. It is an important endogenous signal molecule that can activate plant allergic reactions and system-acquired resistance. Physiological effects in plants are also widely manifested in the regulation of physiological processes such as plant growth, development, maturity, and senescence, and in the induction of anti-stress reactions such as salt resistance, drought resistance, low temperature resistance, ultraviolet resistance, and heavy metal resistance.
2.Glycine betaine
Glycine Betaine is an osmo-protective agent intended for use in home garden, greenhouse and field. It is a natural compound that functions to protect plants from abiotic stress. Conditions like drought, heat, cold, and salt stress cause dehydration and can have a severe impact on crop yield. Osmo-protectants combat these debilitating conditions and improve plant growth and survival. By altering cellular structures and membrane composition they allow plants to adapt to water deficiencies. Studies show that exogenous glycine betaine can be taken up by plant roots and accumulate in leaves, offering normally fragile plants the same protection as those resilient varieties. Glycine betaine is easily dissolved powder that can be applied to foliage or soil to combat dehydration and prevent crop loss.
3.γ-aminobutyric acid
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a four-carbon non-protein amino acid that exists widely in various organisms in a free state. It serves as a signal substance and energy metabolism during plant growth and development. When plants are subjected to adversity stress, GABA can respond quickly and accumulate in large amounts, and the content is increased by more than 10-1000 times compared with normal growth, which can improve plant cell response to adversity stress and enhance plant adaptability.
If you have any interest on above products, please feel free to contact us.
Anne Chou
Email:anne@cyclebioscience.com
Whatsapp:+86 15050351426
Website:www.cyclebioscience.com





评论
发表评论